The 2019 International Narcotics Control Strategy Report (INCSR) is an annual report by the Department of State to Congress prepared in accordance with the Foreign Assistance Act. It describes the efforts of key countries to attack all aspects of the international drug trade in Calendar Year 2018.
Volume I covers drug and chemical control activities. Volume II covers money laundering and financial crimes.
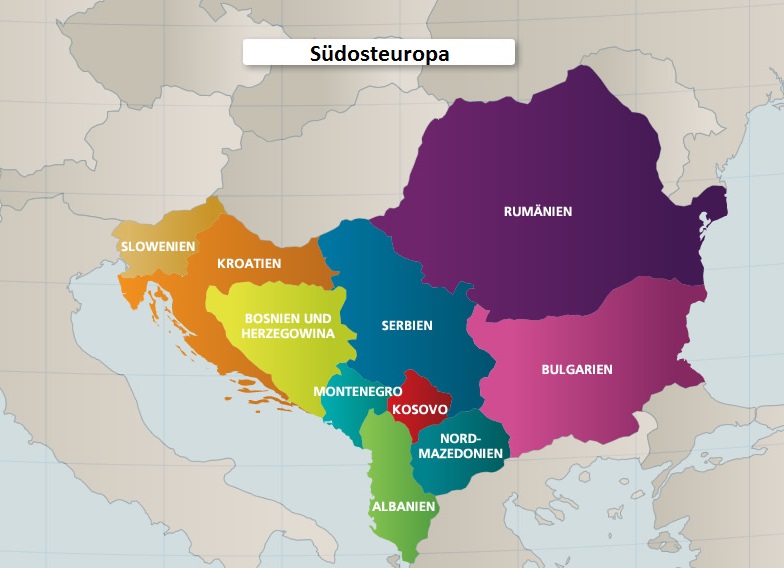
For the third year in row, the report classifies four countries of South East Europe as “major money laundering countries” – those whose financial institutions engage in currency transactions involving significant amounts of proceeds from international narcotics trafficking.

The report notes improvement, but these countries remained on this non-popular list. Here are the resumes of the situation.
The Government of Albania made no significant progress toward thwarting money laundering and financial crimes in 2018. Albania remains vulnerable to money laundering due to corruption, growing organized crime networks, and weak legal and government institutions. The country has a large cash economy and informal sector, with significant money inflows from abroad in the form of remittances. Major proceeds-generating crimes in Albania include drug trafficking, tax evasion, and smuggling. Other significant predicates include counterfeiting, arms smuggling, and human trafficking. Smuggling is facilitated by weak border controls and customs enforcement. Albania serves as a base of operations for organized crime organizations operating in the United States, Europe, the Middle East, and South America. Recent justice reforms, vetting of judges and prosecutors for corruption and ties to organized crime, and the creation of a police task force targeting organized crime activities have created a positive trajectory for Albania to address money laundering and financial crimes. These efforts, however, are still challenged by pervasive corruption.
Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH) has a primarily cash-based economy and is not an international or regional financial center. BiH is in the middle of the Balkans and has open borders with Croatia, Serbia, and Montenegro. A Visa Liberalization Agreement with the EU enables easy transit from Eastern Europe and the Balkans region to countries in Western Europe. BiH is a market and transit point for smuggled commodities, including cigarettes, firearms, counterfeit goods, lumber, and fuel oil.
BiH recently has made substantial progress, not only strengthening its AML regime, but harmonizing its laws across its numerous legal systems, including laws related to money laundering and asset forfeiture. BiH has a complex legal and regulatory framework with criminal codes and financial sector laws at the state and entity levels (Federation of BiH (FBiH) and Republika Srpska (RS)), and in the Brčko District (BD).
BiH completed its National Risk Assessment of Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing in the Period 2018-2022 (NRA) in September 2018, which identifies notaries and real estate agencies as the highest-risk sectors.
In 2018, Serbia made a high-level political commitment to address noted deficiencies and has subsequently made significant progress in bringing its AML regime in line with international standards, resulting in an increased number of related investigations and convictions. With assistance from donors, Serbia updated its national risk assessment (NRA) to better identify current threats or crimes associated with money laundering and methods used to launder money and finance terrorism.
Turkey is an important regional financial center, particularly for Central Asia and the Caucasus, the Middle East, and Eastern Europe. Turkey’s rapid economic growth over the past 15 years combined with its commercial relationships and geographical proximity to areas experiencing political turbulence, such as Iraq, Syria, and Crimea, make Turkey vulnerable to money laundering risks. It continues to be a major transit route for Southwest Asian opiates moving to Europe. In addition to narcotics trafficking, other significant sources of laundered funds include smuggling, invoice fraud, tax evasion, and to a lesser extent, counterfeit goods, forgery, highway robbery, and kidnapping. Recent conflicts on the southern border of Turkey have, to a small extent, increased the risks for additional sources of money laundering. In 2018, Turkey implemented new regulations on the registration and supervision of foreign exchange houses, passed a tax amnesty law, and the government underwent a restructuring, resulting in new ministries.
To read the 2019 International Narcotics Control Strategy Report follow this link>>>>



 The most important results are grouped under headlines:
The most important results are grouped under headlines:

 The objectives of Club Health Amsterdam 2019 include:
The objectives of Club Health Amsterdam 2019 include: To get more information about the Conference,
To get more information about the Conference, 


 In a Recommendation, applicable to both the public and private sectors, the
In a Recommendation, applicable to both the public and private sectors, the 
 The Guidelines are not a ‘toolkit’ for a model drug policy. The Guidelines are a reference tool for those working to ensure human rights compliance at local, national, and international levels, be they parliamentarians, diplomats, judges, policy makers, civil society organisations or affected communities.
The Guidelines are not a ‘toolkit’ for a model drug policy. The Guidelines are a reference tool for those working to ensure human rights compliance at local, national, and international levels, be they parliamentarians, diplomats, judges, policy makers, civil society organisations or affected communities.

 Andriy Klepikov, the Executive Director of the Alliance for Public Health, said that almost half of these funds ($ 5.6 million) will go to the advocacy of the reduction of prices for ARV drugs and optimization of procurement mechanisms. Another quarter of the project budget ($ 3.2 million) is planned for budget advocacy. $ 1.6 million is provided for the removal of legal barriers, the same amount for project management. Another $ 1 million will go to operational research.
Andriy Klepikov, the Executive Director of the Alliance for Public Health, said that almost half of these funds ($ 5.6 million) will go to the advocacy of the reduction of prices for ARV drugs and optimization of procurement mechanisms. Another quarter of the project budget ($ 3.2 million) is planned for budget advocacy. $ 1.6 million is provided for the removal of legal barriers, the same amount for project management. Another $ 1 million will go to operational research.

 The President of the Council of the Nova stranka, Aris Movsesian said that it is normal for the Nova stranka, as well as all other political parties, to sign this declaration. Nova stranka is committed to joining the European Union, and the last year’s European Commission report calls for regulating the treatment of HIV patients, specifically in Chapter 28 where such measures are proposed. Nova stranka also emphasises in point 8 of their Action Plan the problem of relations with vulnerable groups of citizens.
The President of the Council of the Nova stranka, Aris Movsesian said that it is normal for the Nova stranka, as well as all other political parties, to sign this declaration. Nova stranka is committed to joining the European Union, and the last year’s European Commission report calls for regulating the treatment of HIV patients, specifically in Chapter 28 where such measures are proposed. Nova stranka also emphasises in point 8 of their Action Plan the problem of relations with vulnerable groups of citizens.

